MBA Course Outline Comprehensive Guide to Success
MBA Course Outline – MBA Course Artikel serves as your roadmap to understanding the intricate world of Master of Business Administration programs. This Artikel highlights the purpose and significance of MBA courses, delving into available specializations, core components, and elective options that enhance the educational experience. Whether you’re considering an MBA for career advancement or personal growth, this guide provides vital insights into what you can expect.
From practical learning opportunities like internships to the importance of global perspectives, the Artikel emphasizes various teaching methodologies and assessment strategies that shape the MBA experience. You’ll discover how these elements create a dynamic learning environment, preparing students for diverse career pathways.
Introduction to MBA Courses
The Master of Business Administration (MBA) program is designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills, knowledge, and insights to excel in various business environments. The significance of an MBA lies not only in its potential to enhance career prospects but also in its role in fostering a deeper understanding of business dynamics and leadership practices. This program is pivotal for those looking to advance in their current careers or pivot into new industries.There are numerous specializations available within MBA courses that cater to diverse interests and career goals.
Each specialization provides unique insights and skill sets, enabling students to tailor their education to fit their professional aspirations. This flexibility allows graduates to address specific challenges in their chosen fields effectively.
Specializations Available in MBA Programs
MBA programs offer a variety of specializations that align with the evolving demands of the business world. Some of the popular specializations include:
- Marketing: Focuses on strategic marketing, consumer behavior, and digital marketing techniques.
- Finance: Covers investment management, corporate finance, and financial analysis.
- Human Resources: Emphasizes people management, organizational behavior, and talent acquisition.
- Operations Management: Involves supply chain management, process optimization, and quality control.
- Entrepreneurship: Provides insights into starting and managing new ventures, including business planning and innovation.
- International Business: Focuses on global market dynamics, cross-border transactions, and international trade regulations.
These specializations are designed to prepare students for specific roles within their industries, making the MBA a versatile degree suitable for various career paths.
Target Audience for MBA Programs
The target audience for MBA programs typically includes professionals seeking career advancement, entrepreneurs looking to develop their business acumen, and individuals transitioning into managerial roles. MBA programs attract a diverse group of students, including:
- Early Career Professionals: Individuals with some work experience aiming to accelerate their careers and take on leadership roles.
- Mid-Career Professionals: Those looking to enhance their skills and pivot to new industries or higher positions within their current field.
- Entrepreneurs: Individuals aspiring to start their own businesses or innovate within existing organizations.
- Executives: Senior-level professionals seeking to refine their strategic thinking and leadership capabilities.
This diverse audience contributes to a rich learning environment where students can share experiences and insights from various industries.
“An MBA is not just a degree; it’s a transformative journey that equips you with the tools to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape.”
Core Components of an MBA Course

Source: amazonaws.com
An MBA program is designed to equip students with a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape. It blends theoretical knowledge with practical applications, preparing graduates for leadership roles across various sectors. The core components of an MBA course are foundational to this mission, providing essential skills and knowledge that form the backbone of business management.One of the primary aspects of an MBA program is the inclusion of core courses that cover critical business disciplines.
These courses ensure that all graduates possess a well-rounded understanding of the key areas of business, regardless of their specialization. The learning outcomes associated with these core courses enable students to develop analytical skills, strategic thinking, and the ability to work effectively in diverse teams.
Essential Courses in an MBA Program
The essential courses in an MBA program typically include several foundational subjects. These courses are critical in providing students with the necessary skills to navigate the complexities of business management. Below is a list of common core courses and an overview of their respective learning outcomes:
- Accounting Principles: Students learn to interpret financial statements and understand the fundamentals of financial accounting, which is crucial for effective decision-making.
- Finance: This course covers financial analysis, investment strategies, and capital budgeting, empowering students to make informed financial decisions.
- Marketing Management: Students explore market analysis, consumer behavior, and strategic planning to effectively promote products and services.
- Operations Management: Focuses on the efficiency of business operations, teaching students about process optimization and supply chain management.
- Organizational Behavior: This course examines the dynamics of teams and organizations, enabling students to lead and manage effectively.
Learning Outcomes Associated with Core Courses
Each core course in an MBA program is designed with specific learning outcomes that contribute to the overall development of the student. These outcomes typically include:
- The ability to analyze complex business situations and make data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced skills in strategic thinking and problem-solving.
- Proficiency in effective communication and leadership within organizational contexts.
- A comprehensive understanding of financial principles and practices.
- Knowledge of marketing strategies and their application in real-world scenarios.
Subjects Covered Under Finance, Marketing, and Operations Management
In the realms of finance, marketing, and operations management, various subjects are covered that provide depth and rigor to the MBA curriculum.For finance, students might engage with subjects such as:
- Financial Markets and Institutions
- Corporate Finance
- Investment Analysis
- Risk Management
In marketing, the subjects often include:
- Digital Marketing Strategies
- Brand Management
- Consumer Behavior Analysis
- Market Research Techniques
For operations management, key subjects may involve:
- Project Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Quality Control and Improvement
- Service Operations Management
These subjects not only enhance theoretical understanding but also provide practical skills applicable to real-world business challenges.
Elective Courses in MBA Programs
Elective courses play a vital role in shaping the educational journey of MBA students, allowing them to tailor their studies to align with their career goals and interests. These courses enable students to delve deeper into specific areas of business, providing an opportunity to acquire specialized knowledge and skills that can enhance their employability and effectiveness in the workplace.The selection of elective courses can significantly enrich a student’s learning experience by introducing varied perspectives and methodologies.
Electives often cover emerging trends and specialized fields that are not included in core curriculum, allowing students to explore innovative concepts and practices in business. Engaging in these courses can also foster collaboration with peers from diverse backgrounds, further broadening one’s understanding of global business dynamics.
Popular Elective Courses and Their Relevance
A wide array of elective courses is available in MBA programs, each focusing on different dimensions of business education. Understanding these options can help students make informed decisions about their academic paths. Below is a table highlighting some of the popular elective courses, along with their credit hours and prerequisites.
| Elective Course | Credit Hours | Prerequisites |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Marketing | 3 | None |
| Financial Analysis | 3 | Introductory Finance |
| Organizational Behavior | 3 | None |
| Entrepreneurship | 3 | None |
| Supply Chain Management | 3 | None |
| Data Analytics for Business | 3 | Basic Statistics |
The selection of electives is not merely an academic choice; it is a strategic move toward building a successful career. Through electives, students can gain insights into niche areas of interest, such as digital marketing or data analytics, which are increasingly relevant in today’s job market. These courses often incorporate real-world case studies and projects, allowing students to apply their learning in practical scenarios.Furthermore, pursuing electives encourages personal growth and critical thinking.
Students often find themselves challenged to innovate or to approach problems from different angles. The elective courses can also facilitate networking opportunities with industry professionals and peers, thus expanding their professional connections and enhancing career prospects.
“Elective courses provide invaluable opportunities for customization of the MBA experience, enabling students to emerge as well-rounded leaders.”
Course Delivery Methods
The delivery methods used in MBA programs play a crucial role in shaping the learning experience for students. Understanding these methodologies helps in recognizing how various approaches cater to different learning preferences and objectives. The interaction between instructors and students, as well as between peers, is also greatly influenced by the chosen delivery method.
Teaching Methodologies in MBA Programs
MBA programs employ a mix of teaching methodologies to enhance learning. The primary methods include traditional classroom instruction, online learning, case studies, and group projects. Each method has its own unique advantages that contribute to the overall educational experience.
- Traditional Classroom Instruction: This method promotes face-to-face interaction, allowing students to engage directly with instructors and classmates. It often facilitates immediate feedback and deeper discussion on complex topics.
- Online Learning: With the rise of digital technology, many MBA programs have shifted to online formats. This approach provides flexibility, allowing students to access materials and lectures at their convenience. Interaction occurs through discussion boards and video conferencing, making it possible to connect with a global cohort.
- Case Studies: Utilizing real-world business scenarios, case studies allow students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations. This method encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students analyze cases and propose solutions.
- Group Projects: Collaborative projects foster teamwork and communication skills. Students learn to leverage each other’s strengths to achieve common goals, simulating the environment of a professional workplace.
Comparison of Traditional and Online Education Formats
The choice between traditional classroom learning and online education formats can significantly impact the student experience and outcomes. Here are some key differences:
- Interaction Levels: Traditional settings offer higher levels of immediate interaction, while online formats require scheduled discussions, which may lead to delayed responses.
- Flexibility: Online education provides greater flexibility, allowing students to balance work, studies, and personal commitments. Conversely, traditional learning often follows a fixed schedule.
- Learning Environment: In-person classes create a structured environment that can enhance focus, whereas online students must cultivate their own discipline and motivation.
- Resource Accessibility: Online formats can provide a wealth of resources, including recorded lectures and digital libraries, while traditional classrooms may rely on physical textbooks and materials.
Effectiveness of Case Studies and Group Projects
Both case studies and group projects are vital components of MBA curricula, offering experiential learning opportunities that bridge theory and practice. Their effectiveness can be summarized as follows:
Case studies are effective in cultivating analytical skills by challenging students to dissect real business problems.
Group projects enhance teamwork and leadership abilities, essential for future managerial roles.
The integration of these methods not only prepares students for real-world challenges but also fosters a collaborative learning environment. Participating in case studies stimulates strategic thinking, while group projects promote the development of interpersonal skills necessary for successful business practices.
Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
Assessment and evaluation are crucial components of any MBA program, as they not only measure student understanding and proficiency but also provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement. Various methods are employed to ensure a well-rounded evaluation of student performance, taking into account different learning styles and competencies.
Assessment Methods in MBA Courses
MBA programs utilize a diverse array of assessment methods to evaluate students effectively. These methods include traditional exams, group projects, case studies, presentations, and class participation. Each method serves a distinct purpose in gauging student understanding and application of concepts learned throughout the course.To provide a comprehensive view, here are some common assessment methods used in MBA courses:
- Examinations: Formal tests that assess students’ knowledge on specific subjects.
- Group Projects: Collaborative assignments that encourage teamwork and practical application of theories.
- Case Studies: Detailed analyses of real-world business scenarios, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Presentations: Oral reports that allow students to articulate their understanding and findings effectively.
- Class Participation: Active engagement in discussions, which contributes to overall learning and demonstrates understanding.
Grading Criteria for Assignments and Exams, MBA Course Outline
Clearly defined grading criteria ensure that students understand the expectations for their assessments. It also promotes transparency and fairness in the evaluation process. The following grading criteria are typically considered for assignments and exams in MBA programs:
- Content Mastery: Depth and accuracy of knowledge presented in assignments and exams.
- Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze information critically and draw well-founded conclusions.
- Clarity and Structure: Organization of ideas and clarity in presentation, both in written and oral formats.
- Engagement with Sources: Effective use of relevant literature and case studies to support arguments.
- Timeliness: Submission of assignments and completion of projects within the designated timeframes.
Peer Evaluations and Self-Assessments
Incorporating peer evaluations and self-assessments into MBA courses enhances the learning experience by fostering reflection and personal growth. These strategies allow students to gain insights not only from their own work but also from their peers, which can lead to a better understanding of different perspectives and approaches.Peer evaluations involve students assessing each other’s contributions in group projects or presentations.
This practice encourages accountability and hones critical evaluation skills. Similarly, self-assessments prompt students to reflect on their learning journey, identify strengths and weaknesses, and set goals for improvement.
“Peer feedback enhances collaboration and strengthens the learning community within MBA programs.”
Through these assessment tools, students develop a richer understanding of the material and enhance their ability to work effectively in teams, which is vital in today’s business environment.
Importance of Practical Experience
In the realm of MBA education, practical experience plays a pivotal role in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application. It equips students with the necessary skills and insights that cannot be fully grasped through classroom learning alone. Engaging in internships and field projects allows students to apply their academic knowledge in professional settings, enhancing their learning experience and preparing them effectively for their future careers.Experiential learning opportunities are integral to an MBA program’s curriculum.
They not only provide students with hands-on experience but also instill a sense of confidence and professionalism. Participating in internships and field projects enables students to tackle real business challenges and engage with industry leaders, which is invaluable for their career development.
Role of Internships and Field Projects
Internships and field projects are central to the practical learning component of MBA programs. These opportunities allow students to immerse themselves in the business world, where they can observe and participate in day-to-day operations. Here are some notable aspects of these practical experiences:
- Real-World Application: Internships provide students the chance to apply theories learned in the classroom to actual business scenarios, enhancing their understanding of complex concepts.
- Skill Development: Students develop essential skills such as teamwork, communication, and problem-solving, which are critical in any professional environment.
- Portfolio Building: Completing internships or field projects gives students concrete examples of their work, which they can showcase to potential employers.
- Career Exploration: Engaging in various roles allows students to explore different industries and job functions, aiding them in making informed career choices.
Examples of Practical Learning Opportunities
MBA programs offer various practical learning opportunities that enhance the educational experience. These can include:
- Consulting Projects: Students often work on real-life business problems for companies, providing consultancy services while gaining invaluable insights into industry practices.
- Case Competitions: Participating in case competitions allows students to solve business cases in a time-pressured environment, simulating real business challenges.
- Networking Events: Many programs host networking events where students can meet industry leaders, alumni, and potential employers, fostering professional relationships.
Networking and Industry Connections
Networking is a crucial element of MBA programs, as it opens doors to various opportunities and enhances students’ professional connections. The significance of networking can be highlighted through the following aspects:
- Access to Opportunities: Building a strong network can lead to job placements, internships, and mentorship opportunities that may not be publicly advertised.
- Industry Insights: Engaging with industry professionals allows students to gain insights into current trends, challenges, and best practices in their field of interest.
- Peer Learning: Networking with fellow students fosters knowledge sharing and collaboration, enriching the learning experience for everyone involved.
- Alumni Relationships: Maintaining connections with alumni can offer ongoing support and guidance throughout a student’s career, providing a sense of community and belonging.
“Practical experience in an MBA program is not just a supplement to education; it is a foundational pillar that transforms students into capable and confident professionals.”
Career Pathways Post-MBA

Source: meridean.org
For MBA graduates, the completion of their degree often opens doors to a multitude of career opportunities across various industries. This advanced qualification not only equips them with essential business knowledge but also sharpens their leadership and strategic thinking skills, making them highly sought after by employers. Here, we will explore the potential career options available to MBA graduates, share inspiring alumni success stories, and examine salary expectations based on different MBA specializations.
Potential Career Options for MBA Graduates
The versatility of an MBA allows graduates to venture into diverse career paths. The following are notable roles that MBA graduates typically pursue:
- Management Consultant: Many MBA graduates become consultants, providing strategic advice to organizations to improve their performance and efficiency.
- Investment Banker: This role involves advising clients on financial investments and managing assets, often leading to high-salary opportunities.
- Marketing Manager: Graduates often take on roles in marketing, where they develop strategies to promote products and increase brand awareness.
- Operations Manager: Operations roles focus on optimizing processes and managing resources within an organization.
- Entrepreneur: Some MBA graduates choose to start their own businesses, utilizing their education to navigate the challenges of entrepreneurship.
Success Stories of Alumni and Their Career Advancements
Alumni from MBA programs frequently share inspiring stories that highlight the transformative impact of their education on their careers. For example, a graduate from Harvard Business School transitioned from a mid-level position in marketing to the Chief Marketing Officer of a Fortune 500 company within five years of graduation. Similarly, an alumnus of Wharton launched a successful tech startup that secured millions in venture capital funding, underscoring the entrepreneurial opportunities available to MBA holders.These stories not only exemplify individual success but also reflect the broad network and support that MBA programs provide, fostering connections that can lead to significant career advancements.
Salary Expectations Across Various MBA Specializations
Salary expectations can vary significantly based on the chosen MBA specialization. Understanding these differences can help prospective students make informed decisions about their educational paths. Below is an overview of average salaries for various specializations:
| Specialization | Average Starting Salary |
|---|---|
| Finance | $90,000 – $120,000 |
| Marketing | $80,000 – $110,000 |
| Supply Chain Management | $75,000 – $100,000 |
| Information Technology | $85,000 – $115,000 |
| Entrepreneurship | Varies widely; potential for high earnings |
These figures illustrate the lucrative opportunities available to MBA graduates, particularly in high-demand fields. According to the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), MBA graduates tend to earn salaries significantly higher than those with only an undergraduate degree, making the investment in an MBA a worthwhile consideration for many individuals aiming for career advancement.
Global Perspectives in MBA Programs: MBA Course Outline
In today’s interconnected business landscape, the importance of global perspectives in MBA programs cannot be overstated. Understanding international markets and global strategies is essential for aspiring leaders who aim to navigate the complexities of modern commerce. This section delves into the significance of international case studies and global business strategies, as well as the advantages of studying abroad, and the impact of cultural diversity on group dynamics within MBA classes.
Importance of International Case Studies and Global Business Strategies
International case studies are crucial in developing a well-rounded understanding of business practices across different cultures and economies. They provide real-world examples that illustrate how various factors influence business decisions on a global scale. By analyzing these cases, MBA students can learn to apply strategic thinking and problem-solving skills to diverse scenarios. This exposure enhances their ability to formulate effective global business strategies that are adaptable to various market conditions.The incorporation of global business strategies into the curriculum enables students to understand critical concepts such as market entry strategies, international marketing, and supply chain management.
For instance, a case study focusing on a multinational corporation’s approach to entering Asian markets can reveal the challenges and strategies that differentiate success in different regions. These insights foster a deeper understanding of how global economic trends, cultural nuances, and regulatory environments shape business operations.
Benefits of Studying Abroad during an MBA
Studying abroad is an enriching experience that broadens students’ perspectives on global business. It offers unique benefits, including:
- Exposure to International Business Practices: Students gain firsthand experience of different business environments, enhancing their adaptability and resilience.
- Networking Opportunities: Building connections with a diverse array of professionals can lead to valuable career opportunities in international markets.
- Language Skills Development: Immersion in a foreign culture often improves language proficiency, a vital asset in global business communication.
- Personal Growth: Living and studying in a different country fosters independence, cultural sensitivity, and a broader worldview.
These experiences not only enhance the academic journey but also prepare students for leadership roles in a globalized economy.
Impact of Cultural Diversity on Group Dynamics
Cultural diversity within MBA classes plays a significant role in shaping group dynamics and team collaboration. When students from various backgrounds come together, they bring unique perspectives and problem-solving approaches. This diversity fosters creativity and innovation, as different viewpoints often lead to more comprehensive solutions.However, it is essential to recognize the challenges that cultural differences can present. Group members may have varying communication styles, work ethics, and conflict resolution approaches.
Understanding and appreciating these differences is crucial for effective teamwork. To navigate these dynamics successfully, MBA programs often emphasize the importance of cultural competence and emotional intelligence. Students learn to appreciate the strengths that diversity brings to group projects and how to leverage these differences to enhance team performance. Incorporating activities that promote teamwork and understanding of cultural nuances can significantly improve group interactions.
For instance, cross-cultural workshops or team-building exercises can help students develop the necessary skills to work effectively in diverse groups. Overall, embracing global perspectives not only enriches the MBA learning experience but also equips future leaders with the knowledge and skills to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Future Trends in MBA Education

Source: ac.uk
The landscape of MBA education is evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing global economy. As industries adapt to technological advancements and new business paradigms, MBA programs are increasingly incorporating innovative methodologies and emerging trends. These changes aim to enhance the educational experience and equip future leaders with the essential skills needed in today’s business environment.As we delve into the future of MBA education, we observe several key trends reshaping course structures and curricula.
The integration of technology and digital skills has become paramount, redefining how MBA programs prepare students for the complexities of modern business.
Emerging Trends Affecting MBA Course Structures
The transformation of MBA course structures is influenced by various emerging trends that prioritize flexibility, diversity, and real-world applicability. Institutions are now focusing on:
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: MBA programs are increasingly blending business education with fields such as technology, healthcare, and environmental studies. This approach offers students a holistic understanding of how various sectors interact.
- Customization of Curriculum: Many programs now allow students to tailor their coursework to align with their career goals, providing options to specialize in niche areas like data analytics or digital marketing.
- Emphasis on Soft Skills: Alongside technical skills, there is a growing recognition of the importance of communication, leadership, and teamwork, which are essential for effective management.
Importance of Technology and Digital Skills in MBA Curricula
In today’s digital age, the importance of technology within MBA curricula cannot be overstated. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, MBA programs are adapting to include:
- Data Analytics and Big Data: Incorporating courses on data interpretation and analysis equips students with the skills to derive insights from vast datasets, critical for strategic decision-making.
- Digital Marketing Strategies: Understanding online consumer behavior and digital marketing tools is essential as businesses shift towards online platforms.
- AI and Machine Learning: Familiarity with artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies prepares graduates to navigate and implement cutting-edge solutions in various business contexts.
Impact of Remote Learning on Traditional MBA Programs
The rise of remote learning has significantly impacted traditional MBA programs, leading to several notable shifts:
- Increased Accessibility: Remote learning has made MBA education accessible to a broader audience, allowing working professionals to pursue advanced degrees without geographical constraints.
- Hybrid Learning Models: Many institutions are adopting hybrid models that combine online and in-person instruction, providing flexibility while maintaining essential face-to-face interactions.
- Global Networking Opportunities: Virtual platforms facilitate connections with international peers and industry leaders, enriching the learning experience and broadening students’ professional networks.
The integration of technology and remote learning has redefined how MBA programs operate, making them more inclusive and adaptable to the needs of a diverse student body.
Final Conclusion
In summary, the MBA Course Artikel encapsulates the essential framework of MBA programs, showcasing how they equip students with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in today’s competitive business landscape. As you navigate through the various components, remember that an MBA not only offers academic achievements but also lays the groundwork for a successful career, enriched by practical experiences and a global outlook.
User Queries
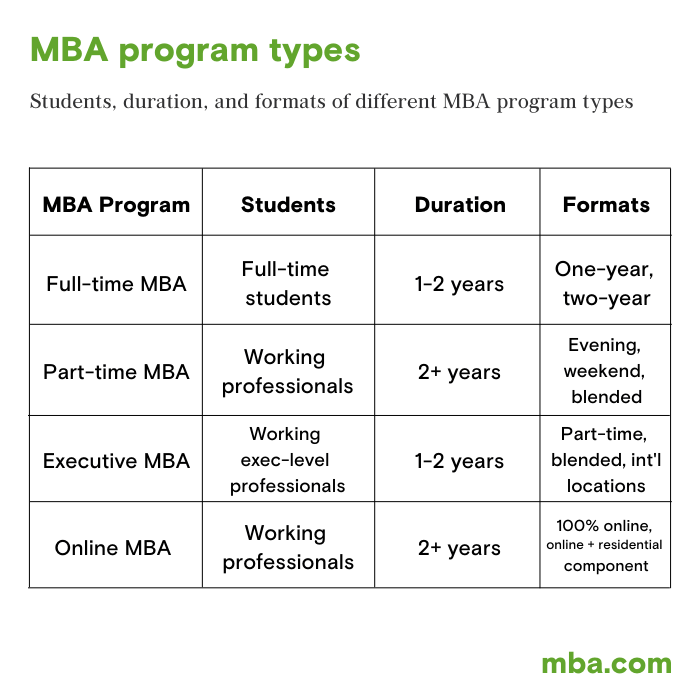
What are the typical durations of MBA programs?
Most MBA programs last between one to two years, depending on whether they are full-time or part-time.
Can I pursue an MBA while working full-time?
Yes, many MBA programs offer flexible schedules, including part-time and online options tailored for working professionals.
What is the difference between an MBA and an Executive MBA?
An Executive MBA is designed for experienced professionals with significant managerial experience, focusing more on strategic leadership than a traditional MBA.
Are there scholarships available for MBA students?
Yes, many institutions offer scholarships based on merit, need, or specific criteria related to professional background or academic excellence.
How important is networking during an MBA?
Networking is crucial in an MBA program, as it helps build connections that can lead to job opportunities and collaborations in the future.