MBA In Operations Management Unlocking Career Potential
MBA In Operations Management sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail. This program is designed to equip students with essential skills and knowledge that are highly valued in today’s competitive business environment. From understanding core concepts to mastering advanced methodologies, the curriculum prepares graduates to tackle real-world challenges in operations across various industries.
As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of efficient operations, the demand for skilled professionals in this field continues to grow. The MBA in Operations Management focuses not only on theoretical knowledge but also on practical applications, enabling graduates to enhance productivity and drive profitability effectively.
Overview of MBA in Operations Management
An MBA in Operations Management is a specialized degree focused on equipping future leaders with the skills and knowledge necessary to oversee and improve an organization’s operations. This field holds significant importance in today’s business landscape as companies increasingly aim to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver quality services and products. The program prepares graduates to tackle complex operational challenges and implement strategic solutions that contribute to organizational success.The core curriculum of an MBA in Operations Management typically includes a blend of theoretical and practical knowledge aimed at developing a comprehensive understanding of operations within various business contexts.
Key subjects covered often include Supply Chain Management, Project Management, Quality Control, Process Optimization, and Inventory Management. These courses provide a robust foundation for students to understand the intricacies of managing resources and processes effectively.
Skills Developed Through the Program
The MBA in Operations Management program cultivates a wide range of skills that are highly applicable in various industries. Graduates are equipped with strategic thinking abilities, analytical skills, and leadership qualities that empower them to drive operational improvements. Key skills developed include:
- Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze complex data and make informed decisions based on quantitative and qualitative insights is crucial in operations management.
- Project Management: Mastering project management principles enables graduates to oversee projects from inception to completion, ensuring they meet deadlines and stay within budget.
- Problem-Solving: The program enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for addressing challenges that arise in operational processes.
- Leadership and Team Management: Graduates learn how to lead teams effectively and foster collaboration, which is vital for successful operations.
- Supply Chain Knowledge: Understanding supply chain dynamics is crucial, as it impacts all aspects of production and service delivery.
The practical application of these skills can be observed in various industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and technology, where efficient operations are integral to success. By leveraging the knowledge and skills gained from an MBA in Operations Management, graduates can significantly contribute to their organizations’ overall performance and competitive advantage.
Career Opportunities
An MBA in Operations Management opens the door to a variety of career paths, making it a valuable degree for those looking to enhance their management capabilities. Graduates can find themselves in dynamic roles that focus on improving efficiency and quality in various sectors. The skills gained from this program are applicable in multiple industries, providing a broad range of opportunities for driven individuals.Operations managers play a crucial role in organizations by overseeing production processes and ensuring that resources are utilized effectively.
Their responsibilities vary significantly based on the sector they are in, encompassing strategic planning to on-ground operational execution. This versatility allows MBA graduates to adapt to different environments, enhancing their employability.
Career Paths Available
Graduates of an MBA in Operations Management can explore various career paths across different sectors. Some of the key positions include:
- Operations Manager: Responsible for overseeing production processes, improving operational efficiency, and managing supply chain logistics.
- Supply Chain Manager: Focuses on optimizing the supply chain from procurement to delivery, ensuring timely and cost-effective processes.
- Project Manager: Manages specific projects within an organization, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
- Logistics Manager: Oversees the transportation and storage of goods, facilitating effective distribution strategies.
- Quality Assurance Manager: Ensures that products meet quality standards, implementing processes to enhance product reliability and performance.
Roles and Responsibilities in Different Sectors
Operations managers are essential in various industries, each demanding unique skills and expertise. Their roles adapt to the specific needs of the sector while maintaining a focus on efficiency and improvement.In the manufacturing sector, operations managers are tasked with streamlining production processes, monitoring equipment maintenance, and optimizing labor productivity. They ensure that operations run smoothly and efficiently, striving to reduce waste and maximize output.In retail, they focus on inventory management, supply chain logistics, and customer service optimization.
Their goal is to enhance the shopping experience while maximizing profits.In healthcare, operations managers oversee the day-to-day functioning of medical facilities, ensuring that patient care processes are efficient and compliant with regulations. They manage staffing, resource allocation, and the implementation of new healthcare technologies.
Companies Seeking MBA Graduates, MBA In Operations Management
Many prominent companies actively seek MBA graduates specializing in operations management, recognizing their potential to drive organizational success. Some noteworthy examples include:
- Amazon: Known for its robust supply chain, Amazon continuously seeks operations managers to enhance logistics and inventory management.
- Procter & Gamble: With a focus on manufacturing efficiency and product quality, P&G values operations expertise in its management teams.
- Deloitte: Often hiring for consulting roles, Deloitte looks for MBA graduates to help clients optimize their operational strategies.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola aims to improve its distribution and production processes, making operations management a critical area for recruitment.
- Walmart: As a retail giant, Walmart consistently searches for operations managers to streamline its vast supply chain and enhance its retail operations.
Comparison with Other MBA Specializations

Source: indiacsr.in
In the ever-evolving landscape of business education, choosing the right specialization is crucial to aligning personal interests with career ambitions. An MBA in Operations Management offers unique advantages and, when compared to other specializations, it highlights different strategic focuses within the realm of business. Understanding these distinctions enables prospective students to make informed decisions regarding their education and future career paths.
Comparison with MBA in Supply Chain Management
While both MBA in Operations Management and MBA in Supply Chain Management focus on efficiency and effectiveness in business processes, their areas of emphasis differ significantly. Operations Management primarily concentrates on the internal processes of an organization, ensuring that resources—such as materials, labor, and technology—are utilized optimally to produce goods and services. In contrast, Supply Chain Management takes a broader view, encompassing the entire flow of goods, information, and finances from the origin of raw materials to the end customer.
This specialization focuses on supplier relationships, logistics, inventory management, and the integration of supply chain activities. Key differences include:
- Focus Area: Operations Management deals with internal operations, whereas Supply Chain Management spans external relationships and logistics.
- Scope: Operations Management is often concerned with process improvement, quality control, and production efficiency; Supply Chain Management emphasizes collaborations, procurement strategies, and distribution networks.
- Skill Set: Graduates in Operations Management typically develop skills in process optimization and operational leadership, while those in Supply Chain Management acquire skills in negotiation, vendor management, and logistics strategy.
Differences Between Operations Management and Project Management
Within the MBA context, Operations Management and Project Management serve distinct functions. Operations Management focuses on the ongoing processes and systems necessary for day-to-day business activities. It involves managing resources, production processes, and service delivery to ensure that operations run smoothly and efficiently.On the other hand, Project Management is centered around specific, temporary endeavors designed to create a unique product or service.
This specialization emphasizes planning, executing, and closing projects within defined timelines and budgets. The differences can be summarized as follows:
- Duration: Operations Management is continuous, while Project Management is temporary and project-specific.
- Objectives: Operations Management aims for efficiency in standard processes; Project Management focuses on achieving specific goals within project constraints.
- Management Approach: Operations Managers maintain ongoing processes, whereas Project Managers lead teams to complete projects successfully.
Complementing Other Business Specializations
An MBA in Operations Management does not operate in isolation; rather, it complements other business specializations such as Marketing and Finance. The integration of Operations Management principles with these fields enhances overall business strategy and effectiveness.For instance, in Marketing, understanding the operational capabilities of a company can significantly influence product development and promotional strategies. Effective operations can lead to better customer service, which is a critical component of successful marketing campaigns.In Finance, operational efficiency directly impacts cost management and profitability.
Operations Managers who understand financial principles can better align operational strategies with financial goals, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively.The synergy between Operations Management and other specializations can be illustrated through the following points:
- Marketing Alignment: Operations insights can improve product delivery and customer satisfaction, enhancing marketing efforts.
- Financial Efficiency: Streamlined operations reduce costs, allowing for better financial performance and investment opportunities.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Knowledge of operations aids in making informed decisions across other business areas, fostering overall organizational growth.
Importance of Operations Management in Business
Effective operations management is a critical component in determining the success of any business. It encompasses the administration of business practices to create the highest level of efficiency possible within an organization. By optimizing resources, streamlining processes, and ensuring a smooth workflow, operations management contributes significantly to the overall performance and competitiveness of a business.The impact of effective operations management on business performance cannot be overstated.
It directly influences cost control, quality assurance, and customer satisfaction, all of which are crucial for a company’s success. By implementing robust operations strategies, businesses can minimize waste, enhance productivity, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Enhancement of Customer Satisfaction and Profitability
Operations management plays a vital role in enhancing customer satisfaction, which is essential for maintaining a loyal customer base and increasing profitability. With a focus on quality and efficiency, organizations can deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. When customers are satisfied, they are more likely to return and recommend the business to others.Several key factors illustrate how operations management contributes to customer satisfaction and profitability:
- Quality Control: Consistent quality in products and services leads to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business.
- Timeliness: Efficient operations ensure that products are delivered on time, which builds trust and reliability.
- Cost Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce costs, allowing businesses to offer competitive pricing without sacrificing quality.
- Flexibility: Effective operations management enables businesses to quickly adapt to changes in customer demand, enhancing responsiveness.
A prime example of a company excelling in operations management is Toyota. The company’s implementation of the Toyota Production System (TPS), which emphasizes just-in-time production and continuous improvement, has led to significant operational efficiencies and outstanding product quality. This operational excellence has not only driven customer satisfaction but also established Toyota as a leader in the automotive industry.Furthermore, Amazon is another case study that showcases the impact of superior operations management.
By leveraging advanced technology and logistics, Amazon has streamlined its supply chain and improved delivery times. The company’s focus on operational efficiency has played a pivotal role in achieving high levels of customer satisfaction, evidenced by its growing customer loyalty and market dominance.
“Efficiency is doing better what is already being done.” — Peter Drucker
The strategic implementation of operations management practices is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in a competitive environment. By prioritizing quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, organizations can significantly enhance their operational performance and drive long-term profitability.
Key Tools and Technologies in Operations Management
In the rapidly evolving field of operations management, leveraging the right tools and technologies is crucial for streamlining processes and enhancing productivity. Understanding and utilizing these resources can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness across various business functions. This section delves into essential software, methodologies, and the transformative role of technology in modern operations management practices.
Essential Software and Tools in Operations Management
The integration of technology in operations management is primarily driven by various software and tools designed to optimize performance. Key tools include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems such as SAP and Oracle streamline business processes by integrating all facets of an operation into a unified system, providing real-time insights and data accessibility.
- Project Management Tools: Software like Trello and Asana facilitate project tracking, resource allocation, and team collaboration, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software: Tools like JDA and Kinaxis help businesses manage their supply chains effectively, from procurement to delivery, ensuring that inventory levels are optimized and costs are minimized.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: BI platforms like Tableau and Power BI analyze data to provide actionable insights, helping organizations make informed decisions based on comprehensive data analysis.
Methodologies in Operations Management
Various methodologies complement the technology used in operations management, providing robust frameworks for improving processes and quality. Notable methodologies include:
- Lean: Lean methodology focuses on minimizing waste without sacrificing productivity, promoting a culture of continuous improvement. It is widely adopted in manufacturing sectors to enhance efficiency.
- Six Sigma: This data-driven approach seeks to improve quality by identifying and removing the causes of defects. Six Sigma uses statistical tools and techniques to measure and enhance process performance.
- Agile: Primarily used in software development, Agile principles can also be applied to operations management, emphasizing flexibility and rapid responses to change, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Transformative Role of Technology in Operations Management
Technology is revolutionizing operations management by automating processes, enhancing data analysis, and improving communication.
“The effective use of technology can lead to enhanced operational efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.”
Modern businesses are increasingly adopting technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to gain a competitive edge. For instance, AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast demand trends, enabling companies to optimize inventory levels and allocate resources more effectively. Similarly, IoT devices facilitate real-time monitoring of equipment and supply chains, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.In summary, the combination of essential software, proven methodologies, and cutting-edge technology is reshaping the landscape of operations management, enabling businesses to achieve their goals with greater precision and efficiency.
Challenges in Operations Management
Operations management is a critical function within any organization, responsible for overseeing the production of goods and services. However, it is not without its challenges. Operations managers often contend with issues such as supply chain disruptions, workforce management, and the need for continuous improvement in efficiency and quality. Addressing these challenges requires strategic thinking and the ability to adapt to a rapidly changing business environment.
Common Challenges Faced by Operations Managers
Operations managers encounter a variety of challenges that can hinder performance and efficiency. Some of these challenges include:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can severely impact supply chains, causing delays and increased costs.
- Workforce Management: Finding, training, and retaining skilled workers is increasingly difficult, especially in industries facing labor shortages.
- Technology Integration: Keeping up with the rapid pace of technological advancement can lead to difficulties in implementing new systems and processes.
- Quality Control: Maintaining product quality while simultaneously reducing costs is a delicate balance that requires constant monitoring and adjustment.
- Customer Expectations: As customer demands evolve, businesses must adapt quickly, which can create pressure on operations to perform efficiently.
To overcome these challenges, operations managers can implement strategies such as enhancing communication across departments, investing in employee training programs, leveraging technology for better data analysis, and fostering strong relationships with suppliers to build resilience in the supply chain.
Impact of Globalization on Operations Management Practices
Globalization has fundamentally transformed operations management, creating both opportunities and challenges for businesses. The interconnectedness of markets allows companies to source materials and labor from various countries, often at lower costs. However, this also introduces complexities in managing operations across different cultures, regulations, and economic conditions.For instance, companies must navigate varying labor laws, tariffs, and trade agreements when operating in multiple countries.
This necessitates a more agile and responsive approach to operations management. Organizations may adopt practices such as just-in-time inventory systems and global sourcing strategies to mitigate risks and enhance efficiency in a global market.
Role of Sustainability and Ethical Considerations in Operations Management
Sustainability and ethical considerations are increasingly vital in operations management. Companies are recognizing the importance of implementing sustainable practices to minimize their environmental impact while meeting consumer demand for responsible business practices. Some key aspects include:
- Resource Management: Efficient use of resources, such as energy and materials, not only reduces costs but also supports sustainability goals.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing processes to minimize waste production aligns with ethical practices and contributes to corporate social responsibility.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical standards fosters trust and can enhance brand reputation in the market.
- Innovation in Processes: Developing new, environmentally friendly products or services can open up new markets and opportunities for growth.
Integrating sustainability into operations management is not just a trend but a necessity for long-term success and competitive advantage in the marketplace. As consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, companies that adapt their operations accordingly can benefit from enhanced loyalty and market share.
Continuing Education and Professional Development

Source: studying-in-germany.org
In the dynamic field of operations management, staying updated with the latest trends, methodologies, and technologies is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Ongoing education and professional development play a crucial role in enhancing one’s skill set and improving career prospects. With the rapid evolution of practices in this area, investing time and resources into continuous learning can lead to greater career satisfaction and advancement.The importance of ongoing education and certifications in operations management cannot be overstated.
It allows professionals to adapt to changes in the industry, understand new tools and technologies, and meet the evolving expectations of employers. Certifications can not only validate expertise but also enhance credibility in the workplace, making candidates more attractive to potential employers.
Resources and Platforms for Professional Development
Numerous resources and platforms are available for professionals looking to further their education in operations management. These resources provide opportunities for learning, networking, and skill enhancement.
- Online Learning Platforms: Websites like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer various courses related to operations management from reputable institutions. These platforms allow learners to study at their own pace and earn certifications upon completion.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations such as the Association for Operations Management (APICS) and the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) provide access to resources, networking opportunities, and certification programs that are invaluable for career development.
- Webinars and Workshops: Many institutions and organizations host regular webinars and workshops on current topics in operations management. These events are excellent for gaining insights from industry experts and enhancing professional networks.
Recommended Books, Courses, and Conferences
Engaging with key literature, courses, and conferences can significantly enhance knowledge and skills in operations management. Below is a curated list that can serve as a valuable resource for professionals in this field.
Books:
- The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement by Eliyahu M. Goldratt – This classic book focuses on the Theory of Constraints and its implications in operations management.
- Operations Management by William J. Stevenson – A comprehensive textbook that covers essential concepts, tools, and techniques in operations management.
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones – This book Artikels the principles of lean management and how to apply them effectively.
Courses:
- Supply Chain Management Specialization on Coursera – An in-depth look at supply chain principles and operations.
- Operations Management: Analysis and Improvement Methods on edX – Focuses on methods to analyze and improve operational processes.
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification
-Various providers offer this certification, which is highly valued in operations management.
Conferences:
- APICS Annual Conference
-Brings together operations management professionals to share knowledge and best practices. - Global Operations Conference
-Focuses on the latest trends and innovations in global operations. - Institute for Supply Management (ISM) Conference
-Offers insights into supply chain management and operations strategies.
“Investing in your education is the best investment you can make in your career.”
Networking and Community Engagement
Establishing a solid network and engaging with the community are crucial for MBA graduates in operations management. Networking helps to exchange ideas, find job opportunities, and foster collaborations, while community engagement enhances personal and professional relationships. Both elements are key in navigating the competitive landscape of operations management.The significance of networking for MBA graduates cannot be overstated. It opens doors to potential job opportunities, partnerships, and mentorships, all of which are invaluable as one navigates the complex field of operations management.
Building a professional network can facilitate knowledge sharing and provide insights into industry trends and best practices.
Engagement with Professional Organizations
Joining professional organizations related to operations management can significantly enhance networking efforts. These organizations not only provide access to a wealth of resources but also facilitate meaningful interactions with industry professionals. Here are some popular organizations to consider:
- APICS (Association for Supply Chain Management): Offers certifications and educational resources focused on supply chain and operations management.
- ISM (Institute for Supply Management): Focuses on advancing the practice of supply management through education and certification.
- ASCM (Association for Supply Chain Management): A global leader in supply chain management that provides training and networking opportunities.
Engaging with these organizations can be done through attending conferences, participating in workshops, and joining webinars. Such activities not only enhance professional knowledge but also facilitate connections with industry peers.
Building a Personal Brand
Developing a personal brand in the field of operations management is essential for standing out in a competitive job market. A strong personal brand reflects one’s skills, expertise, and what one brings to the table. Here are strategies to effectively build a personal brand:
- Create an Online Presence: Establish a professional LinkedIn profile showcasing achievements, projects, and endorsements from colleagues.
- Share Knowledge: Contribute articles or posts on platforms like LinkedIn or industry-related blogs to share insights and demonstrate expertise.
- Engage on Social Media: Follow industry leaders, participate in discussions, and share relevant content to stay on top of trends and expand your network.
- Attend Networking Events: Participate in conferences and local meetups to meet industry professionals and build valuable connections.
Branding oneself as an expert in operations management can be greatly enhanced by showcasing accomplishments, engaging with the community, and actively participating in relevant discussions.
“Networking is not just about connecting people; it’s about connecting people with people, people with ideas, and people with opportunities.”
Conclusion: MBA In Operations Management
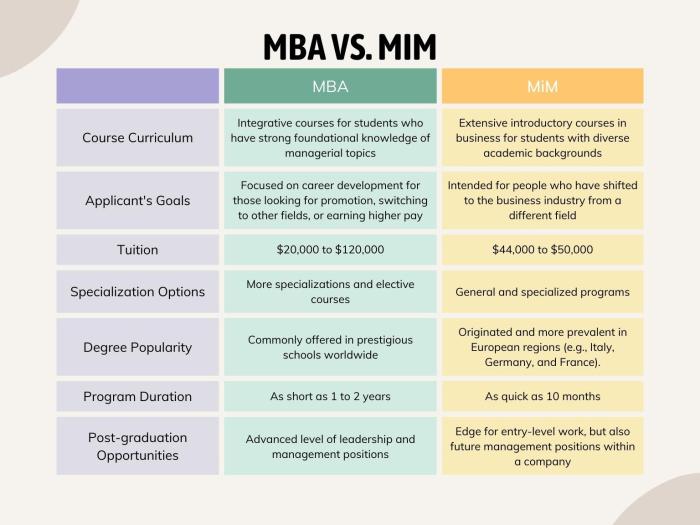
Source: mbastack.org
In summary, pursuing an MBA In Operations Management opens doors to numerous career opportunities and equips individuals with the tools necessary to excel in various sectors. As industries evolve, the role of operations management becomes increasingly critical, driving success and innovation. With a solid foundation provided by this program, graduates are well-prepared to make significant contributions to their organizations and lead the way in operational excellence.
FAQs
What industries typically hire MBA graduates in Operations Management?
Graduates are sought after in various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and retail.
Is work experience required before pursuing an MBA in Operations Management?
While not always required, relevant work experience can enhance the learning experience and career prospects.
What is the average salary for graduates of this program?
Average salaries can vary widely but typically range from $70,000 to over $120,000 depending on the role and industry.
How does this MBA program differ from a regular MBA?
This specialization focuses more on operational strategies and management techniques compared to a general MBA.
Are there online options available for this MBA program?
Yes, many universities offer online MBA programs in Operations Management, providing flexibility for working professionals.