MBA Program Curriculum Unveiling Key Components
MBA Program Curriculum serves as the backbone of advanced business education, shaping future leaders through a thoughtfully designed mix of core subjects and electives. This curriculum is not just a list of courses; it’s a comprehensive framework that prepares students to tackle real-world challenges. From finance to marketing, each core course lays the foundation for critical business skills, while electives offer the flexibility to explore specialized interests, all within a global context.
The structure of an MBA program is crucial as it not only equips students with necessary knowledge but also fosters practical learning opportunities that enhance theoretical understanding. With innovative teaching methods and a focus on collaboration, the MBA curriculum prepares graduates for a dynamic business environment.
Overview of MBA Program Curriculum
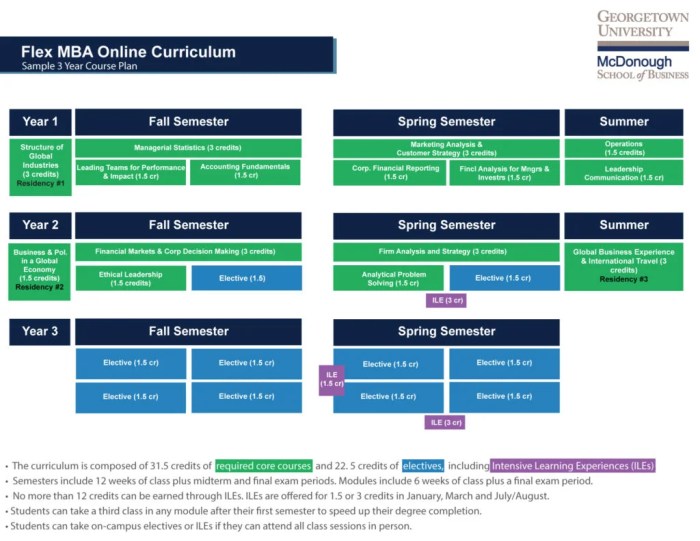
Source: georgetown.edu
The curriculum of an MBA program is a critical element that shapes the educational journey of students pursuing advanced business studies. A well-structured curriculum ensures that graduates are equipped with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary to excel in various business environments. It also plays a vital role in meeting the evolving demands of the job market, preparing students to tackle real-world challenges effectively.The core component of an MBA curriculum typically includes essential courses that provide a strong foundation in key business principles.
These core courses are designed to cover a wide range of topics that are fundamental to understanding the complexities of business management. Common core courses often include subjects such as:
- Financial Management
- Marketing Management
- Operations Management
- Organizational Behavior
- Strategic Management
- Business Ethics
- Data Analysis for Decision Making
These courses not only build a robust understanding of business operations but also enhance analytical and decision-making skills critical for leaders in the corporate world.
Role of Elective Courses in Shaping Education, MBA Program Curriculum
Elective courses in an MBA program provide students with the flexibility to tailor their academic experience to align with their career goals and interests. These courses allow students to explore specialized areas of business, enabling them to gain deeper insights and expertise in specific fields. Electives can range from subjects like Digital Marketing, Entrepreneurship, Supply Chain Management, to International Business.The importance of elective courses lies in their ability to complement the core curriculum and offer practical application of learned theories.
By selecting electives that resonate with their aspirations, students can prepare for specific roles in the workforce. For instance, a student interested in technology management might choose electives in Information Systems and Innovation Management. This tailored approach not only enriches the learning experience but also enhances employability in niche sectors.Additionally, elective courses foster a diverse learning environment where students can collaborate with peers from various backgrounds, sharing perspectives and developing a broader understanding of global business practices.
Through this diversity, students are better equipped to navigate and succeed in the dynamic landscape of modern business.
Core Subjects in MBA Curriculum
The core subjects in an MBA program form the backbone of business education, equipping students with essential skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complex corporate world. These foundational courses cover various aspects of business, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of management practices.The core subjects typically included in MBA programs are Finance, Marketing, Operations Management, Organizational Behavior, and Strategic Management. Each of these subjects contributes uniquely to a student’s skill set, preparing them for various roles in the business environment.
Overview of Core Subjects
The following table compares the core subjects offered by various universities in their MBA programs:
| University | Finance | Marketing | Operations Management | Organizational Behavior | Strategic Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University A | Core | Core | Core | Core | Core |
| University B | Core | Core | Elective | Core | Core |
| University C | Elective | Core | Core | Core | Elective |
Through core courses, students acquire a range of important skills that are crucial for their future careers. For instance, in Finance, they learn to analyze financial statements, manage budgets, and understand investment strategies. Marketing courses teach students about market research, consumer behavior, and brand management. Operations Management covers the principles of supply chain management, process optimization, and quality control. Organizational Behavior focuses on team dynamics, leadership, and communication within an organization.
Lastly, Strategic Management provides insights into long-term planning, competitive analysis, and decision-making processes.
“The foundation of a robust MBA program lies in its core subjects, which are instrumental in developing versatile business leaders.”
Elective Courses and Specializations
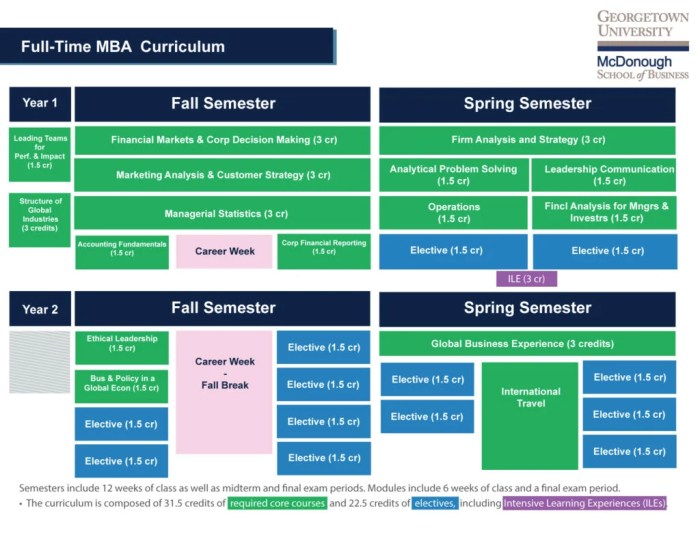
Source: georgetown.edu
In the landscape of MBA programs, elective courses and specializations play a crucial role in shaping students’ career paths and enhancing their skill sets. These offerings provide an opportunity for students to tailor their education according to their interests and career aspirations, adding depth to the foundational knowledge gained from core curriculum subjects.Choosing an elective allows MBA students to explore specific areas of interest in greater detail, equipping them with specialized knowledge that can give them a competitive edge in the job market.
The significance of these specializations extends beyond mere academic enrichment; they also reflect current industry trends and demands, preparing graduates for roles that require specific expertise.
Available Specializations in MBA Programs
A variety of specializations enrich the MBA curriculum, each designed to address specific industry needs and professional goals. Here are some of the popular specializations:
- Marketing: Focuses on consumer behavior, market research, and strategic brand management.
- Finance: Covers investment analysis, corporate finance, and financial markets.
- Human Resources: Emphasizes talent management, organizational behavior, and HR strategy.
- Information Technology Management: Combines business and technology, focusing on IT strategy and digital transformation.
- Operations Management: Centers on supply chain management, production processes, and quality control.
- Entrepreneurship: Encourages innovation and the development of new business ventures.
The significance of these specializations lies in their ability to equip students with targeted skills and knowledge that align with their career ambitions. For example, a finance specialization can prepare graduates for roles in investment banking, while a marketing focus may be ideal for those interested in digital marketing careers.
Popular Elective Courses and Their Focus Areas
Selecting the right elective courses can significantly enhance the MBA experience. Below is a list of some popular elective courses along with their focus areas:
- Digital Marketing: Focus on online marketing strategies, , and social media engagement.
- Data Analytics: Emphasizes data-driven decision-making and uses statistical tools to analyze business data.
- Strategic Management: Concentrates on long-term planning and competitive strategy formulation.
- Business Ethics: Explores ethical dilemmas and moral decision-making in business contexts.
- Global Business: Examines international trade, global markets, and cross-cultural management.
These courses enable students to dive deeper into specific areas, equipping them with the skills needed to tackle real-world business challenges effectively.
Benefits of Electives Versus Core Subjects
While core subjects provide essential business knowledge, electives allow for a more personalized education experience. The benefits of choosing electives over sticking strictly to core subjects include:
- Tailored Learning: Students can focus on areas that align with their career goals and interests.
- Increased Marketability: Specialized knowledge can make candidates more attractive to potential employers in niche fields.
- Networking Opportunities: Electives often attract students with similar interests, providing valuable networking opportunities.
- Interdisciplinary Skills: Electives may encourage skills that span multiple business functions, enhancing overall versatility.
Electives provide a unique opportunity to expand one’s educational horizons, ultimately leading to a well-rounded MBA experience that is both fulfilling and beneficial for future career endeavors.
Practical Learning Opportunities: MBA Program Curriculum
In today’s competitive business landscape, practical learning experiences are essential for MBA students. These opportunities bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application. By integrating hands-on experiences into the curriculum, students develop the skills necessary to navigate complex business challenges effectively.One of the most significant components of practical learning in MBA programs is the inclusion of internships and case studies.
These elements provide students with a platform to apply classroom theories in actual business scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of the material. Internships allow students to work within organizations, gaining insights into the operational and strategic processes that drive success. Case studies challenge students to analyze real business dilemmas and devise actionable solutions, encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Internships and Case Studies
Internships serve as a vital bridge between academic learning and practical application. They offer students the chance to immerse themselves in a professional setting, where they can learn from experienced mentors, gain industry insight, and develop a professional network. The benefits of internships include:
- Exposure to real-world business environments, enhancing understanding of theoretical concepts.
- Opportunities to apply classroom knowledge to solve practical business problems.
- Development of essential soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and leadership.
- Possibility of securing a full-time job post-graduation through networking and performance.
Case studies allow students to engage with real-life business challenges faced by organizations. By analyzing these scenarios, students learn to think strategically and apply various analytical frameworks. The importance of case studies includes:
- Enhancing critical thinking and analytical skills through the examination of complex business situations.
- Fostering collaborative learning through group discussions and presentations.
- Encouraging the application of theoretical concepts in practical settings.
Group Projects and Teamwork
Group projects are an intrinsic part of the MBA curriculum, reflecting the collaborative nature of the business world. These projects not only enhance learning but also simulate real-world dynamics that students will encounter in their careers. The value of group projects includes:
- Development of teamwork and collaboration skills, crucial for success in professional environments.
- Exposure to diverse viewpoints and approaches to problem-solving.
- Improved communication skills as students present their findings and defend their ideas.
Group projects teach students to navigate group dynamics, manage conflicts, and leverage each member’s strengths to achieve a common goal. This experience is invaluable, as the business environment often requires collaborative efforts to drive results.
Hands-On Experiences
Hands-on experiences such as simulations, workshops, and group exercises significantly enhance theoretical knowledge. These immersive experiences allow students to engage actively in the learning process. The benefits of such practical experiences include:
- Immediate application of learned concepts, which reinforces understanding and retention.
- Opportunities to experiment with different strategies and approaches in a controlled environment.
- Feedback from peers and instructors that helps refine skills and understanding.
Through practical learning opportunities, MBA students develop a comprehensive skill set that prepares them for the complexities of the business world. Emphasizing these experiences in the curriculum ensures that graduates are not only knowledgeable but also ready to lead and innovate in their respective fields.
Assessment Methods in MBA Programs
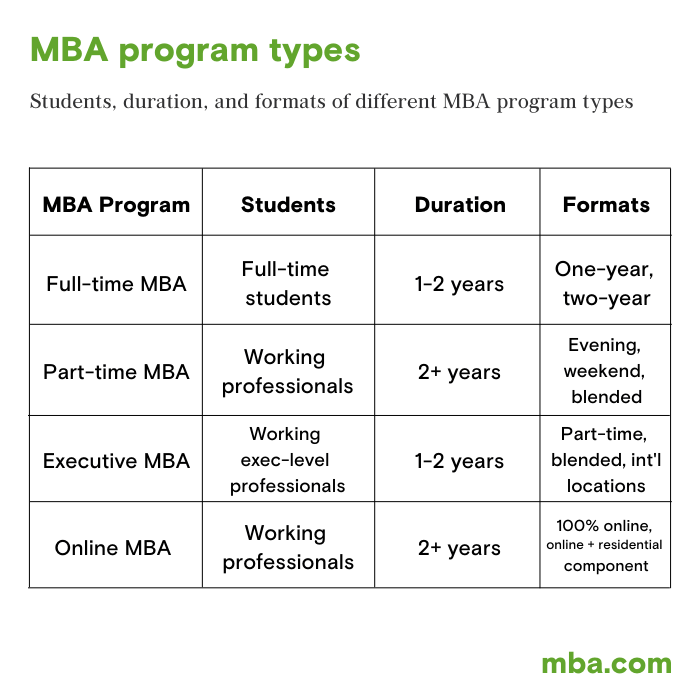
Source: mba.com
Assessment methods in MBA programs are crucial for evaluating student performance and understanding in a variety of key business concepts. These methods encompass diverse approaches such as exams, presentations, and group work, providing a well-rounded measurement of students’ knowledge and skills. Utilizing a combination of assessments not only gauges individual understanding but also encourages collaboration and communication among peers, essential skills in the business world.
Assessment Methods Overview
MBA programs employ a range of assessment methods to accurately measure student learning and engagement. The following methods are commonly used:
- Exams: Traditional written tests or quizzes to evaluate knowledge of core concepts and theories.
- Presentations: Individual or group presentations to showcase understanding of a subject and articulate ideas effectively.
- Group Work: Collaborative projects that assess teamwork, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills.
- Case Studies: In-depth analysis of real-world business situations used to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios.
- Class Participation: Involvement in class discussions and activities, reflecting engagement and contribution to the learning environment.
- Research Papers: Written assignments that require critical thinking and comprehensive analysis of specific business topics.
Weightage of Assessment Methods
The weightage assigned to different assessment methods can vary across institutions and specific courses within an MBA program. Below is a table illustrating a sample distribution of assessment methods and their corresponding weightage in the overall curriculum:
| Assessment Method | Weightage (%) |
|---|---|
| Exams | 30 |
| Presentations | 25 |
| Group Work | 20 |
| Case Studies | 15 |
| Class Participation | 5 |
| Research Papers | 5 |
Importance of Feedback in the Learning Process
Feedback plays a vital role in the learning journey of MBA students. It provides insights into their performance, guiding them on areas needing improvement. Constructive feedback enhances understanding of complex concepts and encourages critical thinking. Additionally, timely feedback allows students to reflect on their work, fostering a growth mindset and continuous learning.
“Feedback is not just about pointing out mistakes; it’s an essential part of the learning process that helps students improve and succeed.”
By integrating diverse assessment methods and valuing feedback, MBA programs aim to create a dynamic learning environment that prepares students for the challenges of the business world.
Trends and Innovations in MBA Curriculum
Recent trends in MBA program curricula reflect a dynamic shift towards integrating technology and innovative teaching methodologies. This evolution caters to the changing needs of the business environment, where adaptability and digital proficiency are crucial. As such, MBA programs are increasingly emphasizing skills that prepare students for the future workforce, focusing on real-world applicability and collaboration across various platforms.A significant trend in modern MBA education is the incorporation of advanced technology and online learning platforms.
The rise of digital tools has transformed how knowledge is delivered and accessed. Blended learning models, which combine traditional classroom experiences with online coursework, have gained popularity. This approach allows for flexible learning schedules and can accommodate a diverse range of students, from recent graduates to mid-career professionals seeking advancement.
Incorporation of Technology and Online Learning
The integration of technology in MBA curricula enhances the learning experience by making it more interactive and accessible. Online learning tools facilitate communication and collaboration among students and instructors, breaking geographical barriers. The following points highlight how technology is reshaping MBA education:
-
Virtual classrooms enable real-time interaction and engagement, fostering a sense of community among remote learners.
-
Learning Management Systems (LMS) provide structured course materials, tracking mechanisms, and resources to promote self-paced learning.
-
Data analytics tools help students understand market trends and consumer behavior, equipping them with the skills needed to make informed decisions.
Innovative teaching methods are also gaining traction in MBA programs. Case studies, simulations, and experiential learning opportunities allow students to apply theoretical concepts in practical scenarios. This hands-on approach not only strengthens understanding but also enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Innovative Teaching Methods
Today’s MBA programs are increasingly utilizing innovative teaching methodologies that promote active learning and real-world application. These methods allow students to engage more effectively with the material and their peers, fostering collaboration and critical thinking. Notable innovative teaching methods include:
-
Flipped classrooms, where students review materials at home and dedicate class time to discussions and practical applications.
-
Project-based learning that encourages teamwork and real-world problem-solving in diverse groups.
-
Guest lectures and workshops led by industry leaders, providing insights into current business practices and challenges.
There exists a distinct contrast between traditional and modern approaches to MBA education. Traditional MBA programs often emphasize theoretical knowledge and standardized testing, whereas contemporary programs focus on adaptability, real-world applications, and collaborative learning environments. This shift not only prepares students for immediate employment but also cultivates lifelong learning habits essential for future career growth.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Approaches
The differences between traditional and modern MBA programs highlight the evolution of educational methodologies in response to the business landscape. Understanding these differences can provide insight into how MBA programs are aligning with industry demands. The following points summarize the key distinctions:
-
Traditional approaches prioritize lecture-based instruction, while modern methods emphasize interactive and participatory learning.
-
Assessment methods have transitioned from exams focused on memorization to evaluations based on projects and presentations, reflecting real-world performance.
-
Networking opportunities and experiential learning are more integral to modern programs, helping students build valuable connections and practical skills.
Global Perspectives in MBA Curriculum
The integration of global business environments into MBA curricula is essential in preparing students for the increasingly interconnected world of commerce. As businesses expand beyond their national borders, MBA programs must equip students with the skills and knowledge to navigate diverse markets and cultural landscapes. This component of the curriculum fosters a comprehensive understanding of international business dynamics, enabling future leaders to make informed decisions in a global context.Global business environments are woven into the MBA curriculum through a variety of approaches that include international case studies, collaborative projects, and the inclusion of global economic perspectives in core subjects.
By examining international market strategies and cross-border operations, students gain insights into how businesses adapt to varying regulatory landscapes, consumer behaviors, and competitive environments around the world.
International Case Studies in Coursework
One of the most effective methods for integrating global perspectives into MBA programs is the use of international case studies. These real-world examples provide students with the opportunity to analyze and solve complex business problems faced by companies operating in diverse regions. Examples of international case studies frequently discussed in MBA programs include:
- Starbucks in China: This case study examines Starbucks’ strategies for entering the Chinese market, highlighting the importance of cultural adaptation and local consumer preferences.
- Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan: Students explore how Unilever applied its global sustainability initiatives in various markets, demonstrating the balance between corporate responsibility and profitability.
- McDonald’s Global Menu Strategy: This case study analyzes how McDonald’s tailors its menu offerings to meet regional tastes and preferences, showcasing the significance of cultural sensitivity in global marketing.
These case studies not only provide practical insights but also encourage students to think critically about the implications of global business practices.
Cultural Awareness and Diversity in Business Education
Cultural awareness and diversity are fundamental components of business education that enhance the learning experience and foster inclusive leadership. Understanding cultural nuances can significantly impact negotiations, team dynamics, and customer relations in a global business environment. MBA programs emphasize the importance of these aspects through various initiatives, such as:
- Global Leadership Projects: Students often participate in projects where they collaborate with international peers, allowing them to experience diverse working styles and communication techniques firsthand.
- Cultural Immersion Programs: Some MBA programs offer opportunities for students to study abroad or engage in internships within multinational corporations, providing exposure to different cultural contexts.
- Diversity Workshops: Workshops and seminars led by experts help students understand the value of diversity in teams and the impact of cultural intelligence on business success.
By cultivating an environment that values cultural awareness, MBA programs prepare students to lead effectively in a diverse and global workforce. This focus on diversity not only enriches the educational experience but also enhances students’ ability to innovate and adapt in various business contexts.
Closing Summary
In summary, the MBA Program Curriculum is a multifaceted framework that combines essential core courses, diverse electives, and practical experiences to cultivate well-rounded business professionals. As the landscape of business education continues to evolve, this curriculum adapts to incorporate new trends and global perspectives, ensuring that students are ready to lead in an ever-changing world.
FAQ Insights
What is the duration of an MBA program?
Typically, an MBA program lasts two years for full-time students, but there are one-year and part-time options available as well.
Are online MBA programs as credible as traditional ones?
Yes, many online MBA programs are accredited and offer the same quality of education as traditional programs, often with added flexibility.
Can I specialize in multiple areas during my MBA?
Some programs allow dual specializations, but it is important to check with the individual program’s policies and requirements.
What types of assessments can I expect in an MBA program?
Students can expect a mix of exams, presentations, group projects, and case studies as part of their assessment methods.
How important is networking during an MBA program?
Networking is crucial as it helps build relationships that can lead to job opportunities and collaborations after graduation.




